
gs Command in Linux
The gs command, short for "ghostscript," is a powerful and widely used PostScript interpreter for Linux and other operating systems. It enables you to view, print, and manipulate PostScript files, which are a common format for vector graphics and page layout.
Table of Contents
Here is a comprehensive guide to the options available with the gs command in linux −
- Understanding the gs Command
- How to use gs Command in Linux?
- gs Command Options
- Examples of ghostscript Command in Linux
Understanding the ghostscript Command
The ghostscript command is a powerful tool for processing PostScript and PDF files in Linux. It offers a wide range of options and flags to control its behavior and output.
Check its version by running the below command −
gs --version

How to use ghostscript Command in Linux?
Ghostscript (GS) is a powerful PostScript interpreter and renderer that can be used to view, print, and manipulate PostScript and PDF files on Linux systems.
gs Command Options
Here are some of the most commonly used options −
| General Options | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| -d | Sets a device parameter. There are numerous device parameters available to control various aspects of the output, such as page size, orientation, resolution, and color space. |
| -r | Sets the output resolution in dots per inch (dpi). |
| -h | Displays the help message, providing a list of all available options. |
| -v | Enables verbose output, showing detailed information about the processing. |
| -q | Suppresses most output, providing a quiet mode. |
| Input / Output Options | |
| -sDEVICE=device | Specifies the output device to use. Possible devices include ps, pdf, png, jpeg, and many others. |
| -sOutputFile=filename | Sets the name of the output file. |
| -dBATCH | Processes the input file without prompting for user interaction. |
| -dNOPAUSE | Disables pauses between pages. |
| Processing Options | |
| -dNoOutput: | Processes the input file without producing any output. |
| dFirstPage=number | Sets the first page to process. |
| -dLastPage=number | Sets the last page to process. |
| -dNumCopies=number | Sets the number of copies to print. |
| -dOrientation=portrait|landscape | Sets the page orientation. |
| -dPageScaling=factor: | Sets the page scaling factor. |
| -dFitPage | Scales the page to fit the output device. |
Examples of ghostscript Command in Linux
Here are some common examples of how to use ghostscript Command in Linux −
ghostscript (GS) is a powerful PostScript interpreter and renderer that can be used to view, print, and manipulate PostScript and PDF files in Linux systems.
gs

Viewing a PDF File
To view a PDF file in ghostscript, you can use the following command −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -sOutputFile=output.pdf input.ps

This command tells ghostscript to run in safe mode (-dSAFER), process all pages without pausing (-dBATCH and -dNOPAUSE), set the device to PDF writing (-sDEVICE=pdfwrite), and specify the output file (-sOutputFile=output.pdf) for the input PostScript file (input.ps).
Converting a Document to an Image
To convert a PS or PDF document to an image format like PNG, use −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -sDEVICE=png16m -r300 -sOutputFile=output.png input.pdf

Here, -sDEVICE=png16m sets the output format to 24-bit color PNG, -r300 sets the resolution to 300 DPI, and output.png is the name of the resulting image file.
Merging PDF Files
ghostscript can merge multiple PDF files into a single file with the following command −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -sOutputFile=merged.pdf input1.pdf input2.pdf

The input1.pdf, input2.pdf, are the source files that will be merged into merged.pdf.
Reducing PDF File Size
To reduce the size of a PDF file by compressing images within it, you might use −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -dCompatibilityLevel=1.4 -dPDFSETTINGS=/screen -sOutputFile=compressed.pdf input.pdf

The -dPDFSETTINGS=/screen option sets a lower resolution and quality for images, suitable for viewing on a screen, thus reducing the file size.
Extracting Pages from a PDF
If you need to extract certain pages from a PDF, the following command can be used −
gs -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -dNOPAUSE -dBATCH -dSAFER -dFirstPage=1 -dLastPage=1 -sOutputFile=extracted.pdf input.pdf

This command extracts the first page from input.pdf and saves it as extracted.pdf. You can change the values of -dFirstPage and -dLastPage to extract different pages.
Converting PostScript to PDF
For converting a PS file to a PDF, you can use −
ps2pdf input.ps output.pdf

ps2pdf is a script that comes with Ghostscript, which simplifies the process of converting PS files to PDF format.
Ghostscript (GS) is a powerful PostScript interpreter and renderer that can be used to view, print, and manipulate PostScript and PDF files in Linux systems via the help page −

Viewing a PostScript or PDF file
Here, it enables a safer mode to prevent malicious PostScript code from being executed. -dBATCH: Disables interactive mode, allowing the command to run without user input. -dNOPAUSE: Prevents the viewer from pausing after each page. -q: Suppresses most output.
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -q input.pdf

Printing a PostScript or PDF file
Now, specifies that the output should be sent to a printer. -sPrinter=myprinter: Sets the name of the printer to use −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -q -sDEVICE=printer -sPrinter=myprinter input.ps

Converting a PostScript file to PDF
Now, specifies that the output should be a PDF file. -sOutputFile=output.pdf: Sets the name of the output PDF file −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -sOutputFile=output.pdf <filename.ps>

Converting a PDF file to PostScript
Specifies that the output should be a PostScript file. -sOutputFile=output.ps: Sets the name of the output PostScript file −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -sDEVICE=pswrite -sOutputFile=output.ps input.pdf

Adding a watermark to a PDF file
This command adds the text "Watermark" to the center of the PDF file. You can customize the font, size, and position of the watermark as needed −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -sDEVICE=pdfwrite -sOutputFile=output.pdf -dDEVICEWIDTH=612 -dDEVICEHEIGHT=792 -dSAFER -dNOPAUSE -q -c "<</Font <</F1 5 0 R>> /Font << /F1 1 0 R>> setdict>> setpagedevice" -c "100 700 moveto (Watermark) show" <filename.pdf>

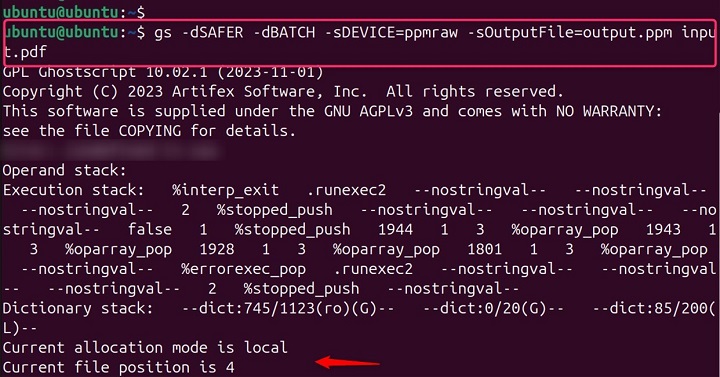
Extracting images from a PDF file
This command extracts the images from the PDF file and saves them as PPM (Portable Pixmap) files. You can then convert PPM files to other formats using tools like ImageMagick −
gs -dSAFER -dBATCH -sDEVICE=ppmraw -sOutputFile=output.ppm input.pdf
These are just a few examples of what you can do with Ghostscript on Linux. The tool is highly versatile and supports a wide range of options and devices, making it a staple in many document processing workflows. For a more comprehensive list of commands and options, you can refer to the official.
Conclusion
Ghostscript is a powerful tool used for processing PostScript (PS) and Portable Document Format (PDF) files. It has a variety of uses, from viewing and converting files to more complex tasks like combining documents.