App crashes, slow load times, and laggy interfaces are top reasons users abandon mobile apps.
Overview
What is Mobile App Performance Testing?
It is the process of assessing how a mobile app behaves under varying load, device, and network conditions to ensure speed, stability, and responsiveness.
Why Mobile App Performance Testing Is Important
Even minor performance issues can lead to poor reviews and uninstalls. Early testing helps identify and fix bottlenecks before they impact users.
Mobile App Performance Testing Checklist
- Cross Platform Compatibility: Works across Android, iOS, and OS versions
- Cross Device Compatibility: Functions smoothly on all screen sizes and resolutions
- Average Load Speed: Loads within acceptable time limits across conditions
- Load Bearing Capability: Handles expected user volume without slowing down
- Stress Testing: Identifies the app’s breaking point under pressure
- Spike Testing: Tests behavior during sudden traffic surges
- Interruption Handling: Maintains performance during calls, messages, or network changes
- Reliability Testing: Ensures consistent functionality across environments
This article covers everything you need to know about mobile app performance testing, including tools, test planning, challenges, and best practices.
What is Mobile App Performance Testing?
Mobile app performance testing evaluates how an app behaves under different load conditions, environments, and usage scenarios. It measures speed, responsiveness, stability, and resource usage to ensure a seamless user experience across
Why Mobile App Performance Testing Is Important
Performance issues can lead to crashes, delays, and frustrated users, ultimately impacting app ratings and business success.
Performance testing helps teams proactively address these risks by:
- Detecting and eliminating performance bottlenecks before release
- Ensuring consistent behavior across varying loads and conditions
- Improving user satisfaction, engagement, and retention
- Validating app scalability across devices, OS versions, and networks
- Reducing the likelihood of crashes and critical issues in production
By identifying issues early, teams can deliver a stable, high-performing app experience in real-world conditions.
Must Read: Top 20 Performance Testing Tools in 2025
Key Performance Metrics to Monitor
Tracking the right metrics is essential for identifying performance issues and validating improvements. These metrics reflect the app’s behavior in real-world user scenarios.
- App launch time: Time taken from tapping the app icon to usability.
- Response time: Time to respond to user interactions like taps or gestures.
- CPU usage: Percentage of processor power consumed by the app.
- Memory usage: RAM consumption during app execution.
- Battery usage: Impact on battery life during prolonged usage.
- Network latency: Delay in data transmission during server/API calls.
- Error rate: Frequency of failed requests or crashes during normal and peak usage.
- Frame rate (FPS): Smoothness of UI animations and screen transitions.
Must Read: Response Time Testing in Software Testing
Types of Performance Tests for Mobile Apps
Different performance tests target specific aspects of app behavior under varied conditions. Combining these tests ensures comprehensive performance coverage.
- Load Testing: Measures how the app performs under expected user loads.
- Stress Testing: Determines the app’s breaking point by pushing it beyond normal capacity.
- Spike Testing: Assesses how the app handles sudden, extreme increases in traffic.
- Soak Testing: Evaluates app performance over an extended period to identify memory leaks or degradation.
- Volume Testing: Tests how the app handles large amounts of data or transactions.
- Endurance Testing: Verifies stability and performance consistency over prolonged usage.
Mobile App Performance Testing Checklist
Here is a comprehensive checklist for mobile app performance testing:
1. Cross Platform Compatibility
If you expect your app to be used internationally or even nationally, it must be optimized for perfect compatibility with different mobile platforms and operating systems. Just because the app works perfectly on Android 5.0 Lollipop does not mean it will work just as well on Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich – not by default, at least.
- You must put your app through comprehensive tests while it runs on multiple versions of mobile operating systems – Android, iOS, Windows, etc.
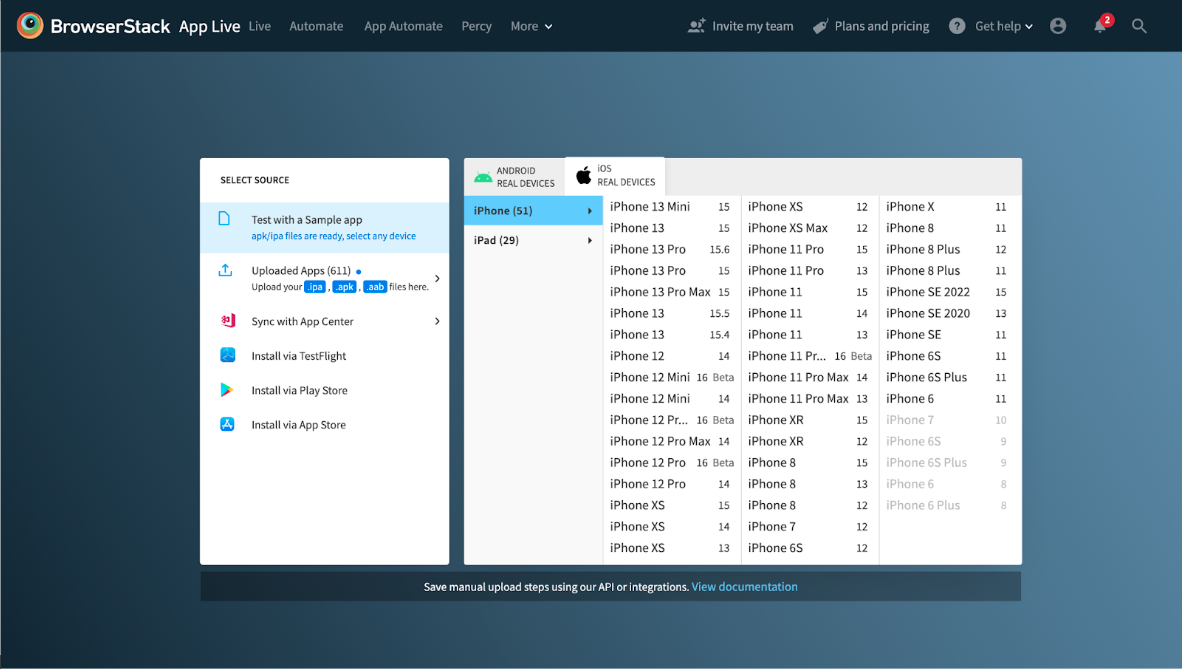
- If you’re trying to find an easy way to test on multiple OSes (including different versions) without having to download, install and configure them, you might try the BrowserStack cloud.
2. Cross Device Compatibility
As with mobile OSes, your device must render and perform perfectly on thousands of mobile devices with varying screen sizes, resolutions, settings and configurations for hardware and software. Again, your app’s behavior must be verified through mobile app testing on real mobile devices – phones and tablets.
Don’t forget to verify the app’s responsive design as you upload and operate it on multiple devices. The big advantage of BrowserStack App Live is that you can upload your app once and then simply switch between different devices without re-installing the app under test.
3. Average Load Speed
Much like websites, mobile apps too must load within seconds to retain user interest.
Naturally, an app only performs well if it is loading within a couple of seconds or whatever device or OS is used to access it. As with the above two points, the best way to gauge current load speed is to check how your app loads on different real devices.
- Don’t forget that your app will probably work under varied network conditions.
- Your test infrastructure should allow you to perform network throttling to monitor app performance at lower network strengths like 2G or Edge.
Read More: Performance Testing: A Detailed Guide
4. Load Bearing Capability
Mobile apps should be able to function even when they are bombarded by an unusually high number of user requests.
For example, let’s say that an airline booking app has to deal with millions of people trying to change or cancel their flights due to a natural disaster that occurred recently. With thousands or perhaps millions of users trying to operate the app simultaneously, does it still work as expected? Or does it crash?
- Load Testing answers these questions after which developers identify optimization opportunities to deal with expected load, and perhaps even a little higher just to be safe.
- With every iteration, load tests identify and remove performance bottlenecks under specific user volumes, leading to greater stability and functionality under stress.
5. Stress Testing
Stress tests usually go in tandem with load tests. In this case, the app will be inundated with simulated user requests until it breaks. The point of such a test is to identify the app’s breakpoint so that it can be optimized to accommodate more requests.
For example, let’s say that the aforementioned airline app needs an upgrade after a natural disaster incident. The dev team wants to check exactly at what number of user requests it finally stopped functioning, how app function slowed down, and at what number the app performed so badly that users started to bounce.
This is accomplished through Stress Testing.
Read More: What is Monkey Testing
6. Spike Testing
Spike testing evaluates how an application handles sudden, short-term surges in user traffic. Unlike load or stress testing, it focuses on abrupt increases rather than sustained pressure.
For instance, during events like Black Friday, an e-commerce app may face a rapid spike in users. Spike testing helps determine if the app can maintain performance under such sudden load changes.
It is useful for apps expecting occasional traffic peaks, as it avoids the cost and complexity of optimizing for consistently high loads.
7. Interruption Handling
In the real user conditions, mobile apps have to deal with numerous interruptions – incoming calls, messages & notifications from other apps, to name a few. To verify how an app works when dealing with such interruptions, you must test them in those specific conditions.
Remember that each interruption scenario while testing native apps must be checked across devices, OSes, and network conditions. Ideally the app should work well even when a call comes in when network conditions are less than perfect.
8. Reliability Testing
Reliability tests check if an app fulfills its intended purpose in different environments. It encompasses most of the other pointers, but it also requires a few more tests. Common reliability tests include:
- Security Testing
- Functional Testing
- Regression Testing
- Testing integration with third-party sites and apps
- Regulatory Testing
Essentially, reliability tests check how dependable the app is in varied real user conditions. Are its security mechanisms fool-proof when deployed in a location where they’re likely to deal with more hacking attempts? When used in a country with tighter data privacy regulations, does the app actually protect user data as required by local legislation? Your answers lie with reliability testing.
Read More: How to test Banking Apps?
Popular Tools for Mobile App Performance Testing
Choosing the right tools is essential for accurately simulating real-world usage and uncovering performance issues early.
Here are some of the most widely used tools for mobile app performance testing:
- BrowserStack App Performance: Enables testing on 3,500+ real devices and browsers, with features like network throttling, geolocation, and debugging tools.
- Android Profiler (Android Studio): Monitors CPU, memory, and network usage in real time during test runs on Android apps.
- Xcode Instruments: Offers detailed performance diagnostics for iOS apps including memory leaks, battery usage, and GPU performance.
- Firebase Performance Monitoring: Tracks app startup time, network latency, and screen rendering performance for Android and iOS apps.
- Apache JMeter: A popular open-source load testing tool for APIs and backend services, often used in mobile app performance pipelines.
- New Relic: Provide end-to-end performance monitoring with real-time insights across frontend and backend services.
Building a Mobile App Performance Test Plan
A structured test plan ensures consistent, repeatable results and helps teams catch issues before they reach production.
Here’s how to build an effective performance test plan:
- Define performance goals: Set measurable KPIs such as response time, memory usage, or acceptable crash rate.
- Identify key user scenarios: Focus on high-traffic features like login, checkout, or in-app search.
- Select performance metrics: Choose metrics aligned with your goals (e.g., load time, CPU usage, API latency).
- Choose testing tools and environments: Use real-device platforms like BrowserStack to simulate real user conditions.
- Create test scripts: Design tests for normal, peak, and extreme load conditions, using automated and manual methods.
- Execute tests iteratively: Run tests across various device and network combinations throughout the dev cycle.
- Analyze and act: Review results, identify bottlenecks, and work with dev teams to implement optimizations.
Also Read: Guide to UI Performance Testing
Common Challenges of Mobile App Performance Testing (With Solutions)
Performance testing mobile apps is critical but comes with its own set of challenges. Here’s how to address them effectively:
- Device fragmentation: Testing across many OS versions and device types is complex.
Use real device clouds to cover various devices without maintaining in-house labs. - Network variability: Simulating real-world network conditions like 3G or low bandwidth is difficult. Use tools that support network throttling and latency simulation.
- Unstable tests and flakiness: Intermittent test failures lead to unreliable results. Use stable element locators and structured test scripts with retry logic.
- Limited visibility into backend issues: Slowdowns in the backend may affect frontend performance. Combine UI testing with API monitoring and backend load testing tools.
- Time-consuming test cycles: Running tests on multiple devices can delay releases. Run tests in parallel across real devices using platforms like BrowserStack.
Read More: What is Android Performance Testing?
Best Practices for Mobile App Performance Testing
Following proven performance testing practices ensures high-quality, stable apps that scale with user demand. Keep these principles in mind:
- Start performance testing early in the development lifecycle
- Test on real devices under real network conditions
- Use a mix of manual and automated tests for broad coverage
- Simulate realistic user journeys with varied data and device types
- Monitor key metrics continuously, not just before release
- Automate repetitive tests and integrate them into your CI/CD pipeline
- Continuously analyze results and update test cases to reflect app changes
Conclusion
Mobile users expect fast, seamless experiences; any delay, crash, or lag can quickly lead to uninstalls and poor reviews.
Performance issues are among the most visible and damaging, making them a top priority during testing.
The checklist above offers a solid baseline for evaluating app performance under real user conditions. While additional tests may vary by use case, these core checks are essential for delivering stable, high-performing apps and accelerating release cycles.